Code Context
The Code Context feature allows you to upload code files that are currently open in your workspace to the CodeVista context system (Supported coding file type: C, C++, Java, JavaScript, PHP, Python, Ruby, Go , ust, TypeScript, Kotlin). This provides context for features like code chatting, command prompting, and predefined workflows. Follow these steps to use the Code Context feature:
Code Context Workspace
- In CodeVista Chat Conversation Panel, click the Code Context button in the navigation bar
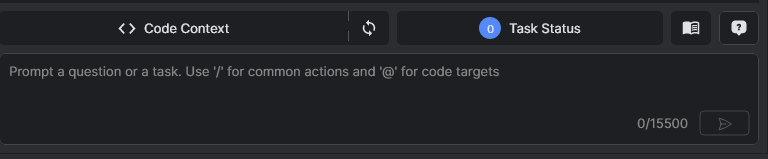
- The Code Context interface will appear.
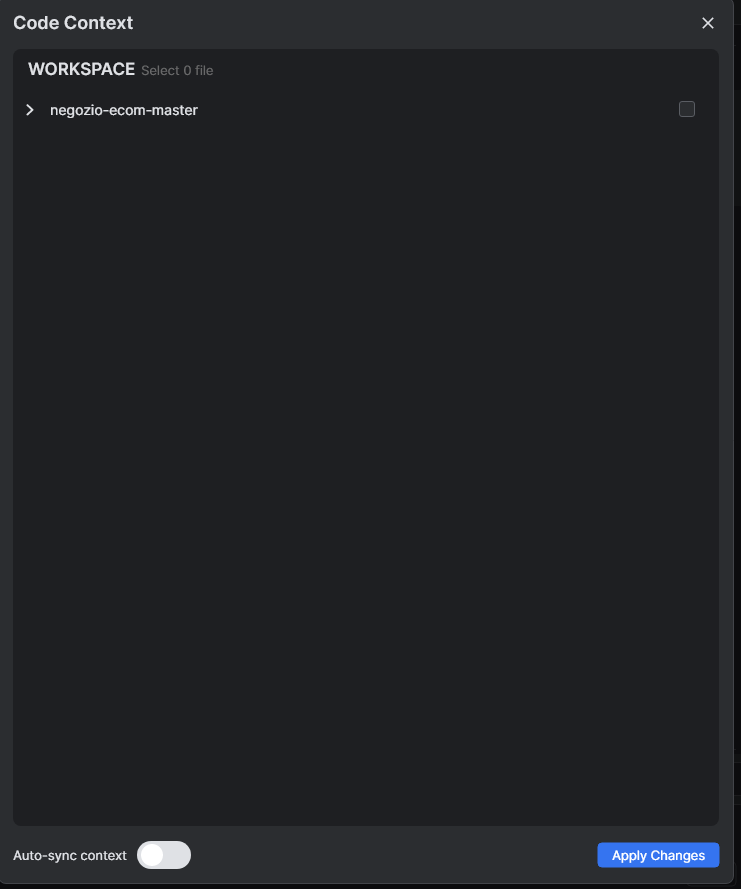
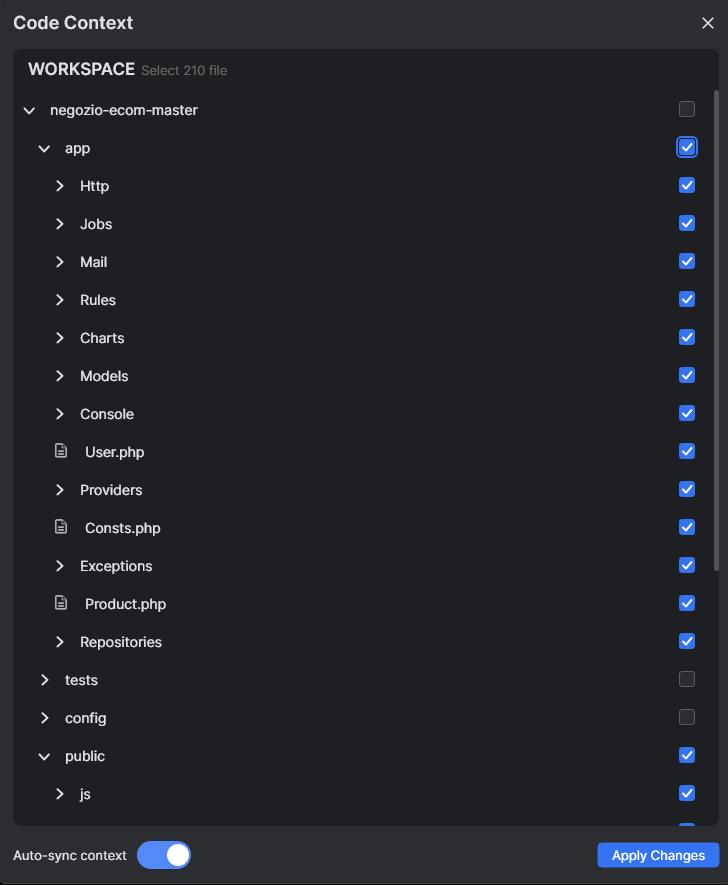
Upload Code Files
-
In the Code Context interface, check the boxes next to the code files you want to upload.
-
After selecting the files, click the Apply button.
- CodeVista will upload and process the selected files.
- Currently, CodeVista supports 57 file types and provides Code Symbols Parsing for 12 file types:
- .java
- .js
- .php
- .cs
- .c
- .cpp
- .rb
- .kt
- .go
- .rs
- .py
- .ts
Manage Uploaded Files
- While you make changes to your code files, it's likely that you would like to sync the latest file changes to the Code Context. You can do this by clicking on the Sync icon
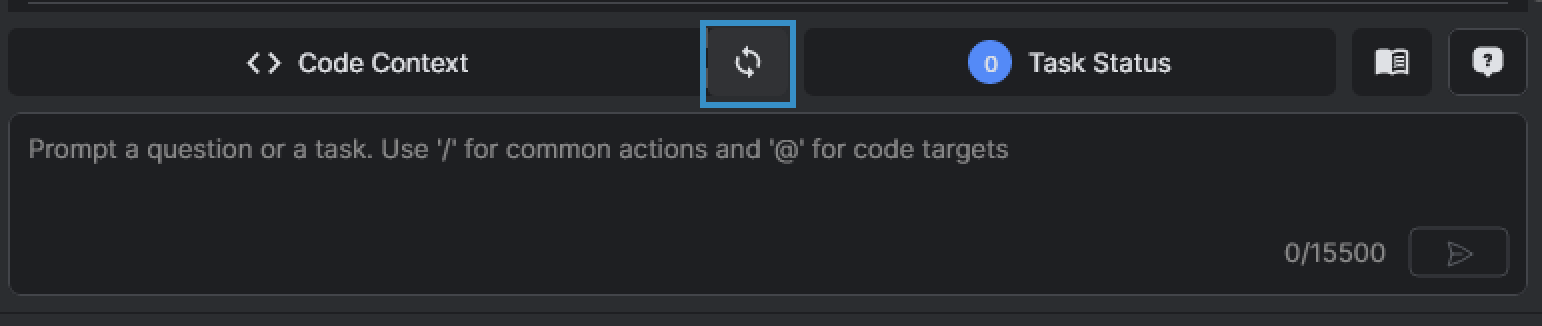
- Or you can also turn on the Auto-sync context to automatic apply changes to the code context.To delete a file from the CodeVista system, check the boxes next to the files and click Apply to remove the file from code context.
- After uploading and processing your code files, you can use other CodeVista features like code chatting, command prompting, or predefined workflows with the context from the uploaded code files.
Code Symbol References
After CodeVista finished indexing the code context, the code entities within the uploaded files will be available for the Action Commands
Below are some supported code entities:
-
@file:fileName -
@function:functionName -
@class:className
You can chain an Action Command to the indexed entities: For example:
Explain the purpose of @function:get_image_download_link
By mastering the grammar of Action Commands and Code Entities, you can significantly improve your workflow efficiency.